Med info
Symptoms of Keratitis and Key Facts About Corneal Inflammation
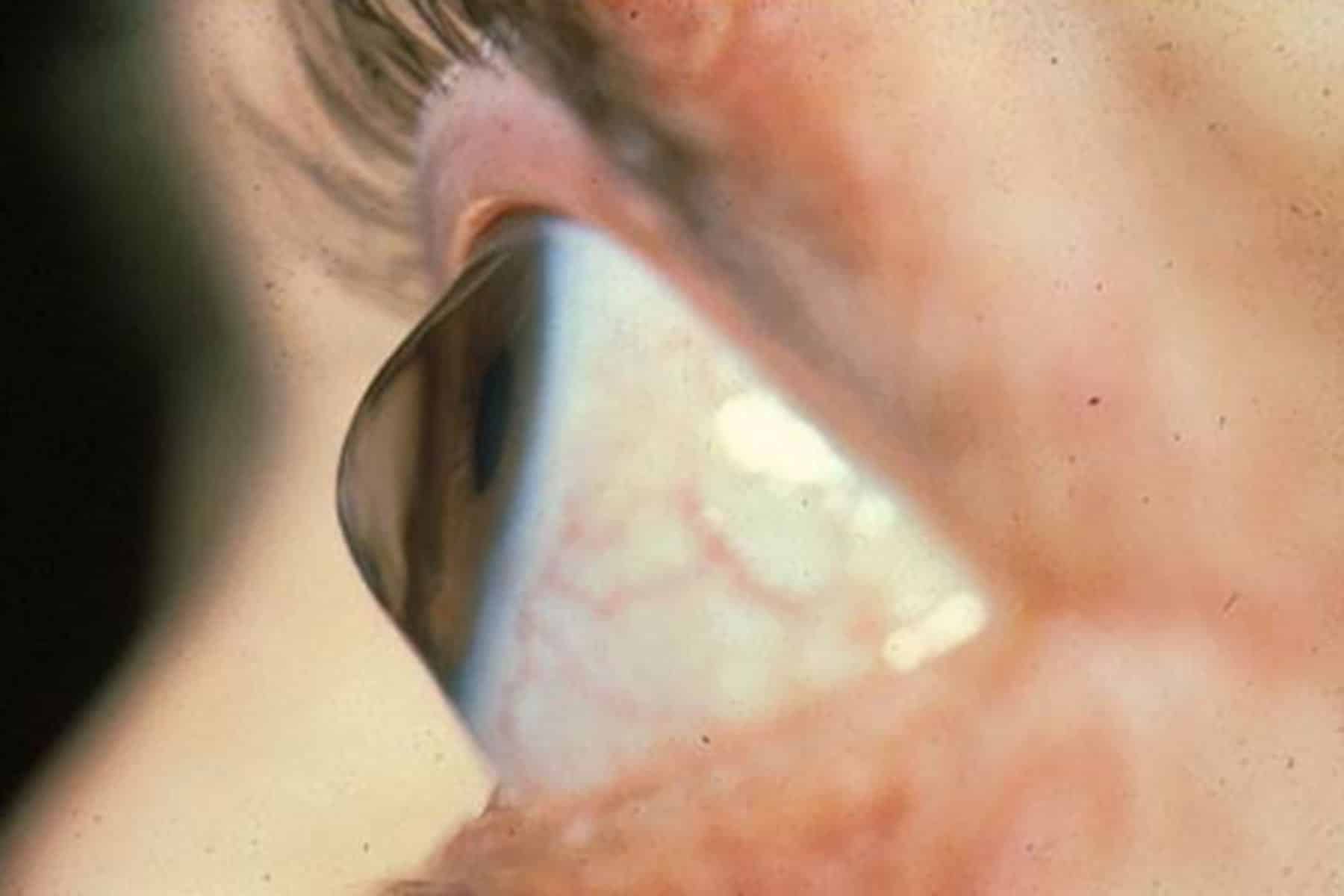
Keratitis is a medical term that refers to inflammation of the cornea. Common symptoms of keratitis include sudden onset of eye pain, eye redness, itching, blurred vision, tearing or discharge from the eye, and sensitivity to light (photophobia).
Infectious keratitis is one of the leading causes of preventable blindness worldwide. It occurs more frequently in developing countries, with an estimated global incidence of about 500,000 cases per year.
Read also: Corneal Transplant Surgery: Everything You Need to Know About This Procedure
What Causes Keratitis?
The most common causes of keratitis are trauma and infection. However, keratitis can also be non-infectious and may develop secondary to a wide range of other conditions. In a completely healthy eye, corneal infections are relatively rare.
Viral, fungal, parasitic, and bacterial infections are more likely to occur after minor trauma or insult to the corneal surface. This happens because the normal defense mechanisms of the cornea are disrupted, allowing bacteria or other microorganisms to invade when there is an epithelial defect (such as a corneal abrasion).
These organisms may originate from the tear film, foreign bodies, contact lenses, or irrigation solutions. Corneal destruction can progress rapidly (within 24 hours in the case of highly virulent organisms), so prompt recognition and early treatment are critical to prevent vision loss.
Keratitis can be caused by a variety of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. Bacteria are the most common cause of infectious keratitis.
The most frequently implicated bacterial groups in bacterial keratitis are Streptococcus species, Pseudomonas, Enterobacteriaceae (including Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia, and Proteus species), and Staphylococcus species.
Other contributing factors that may influence the severity of the condition include the degree of trauma, the presence of underlying ocular surface disease, the use of topical corticosteroids or contact lenses, the host immune response, and the time taken to establish a diagnosis and initiate treatment.
Read also: Intraocular Lens Implantation and What You Need to Know
The Most Common Symptoms of Keratitis
The most important and common symptoms of keratitis include:
– Sudden eye pain
– Redness of the eye
– Itching or irritation
– Blurred or decreased vision
– Excess tearing or discharge from the eye
– Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
– The sensation of a foreign body in the eye
– Difficulty keeping the eye open
Read also: Treatment of Retinal Diseases and Surgery | Management of Dryness, Redness, and Eye Inflammation
Risk Factors for Keratitis
The most common risk factors for developing keratitis include:
– Wearing contact lenses (especially with poor hygiene or overnight wear)
– Eye trauma or foreign bodies in the eye
– Pre-existing ocular surface disease (such as dry eye or blepharitis)
– Previous eye surgery
– Use of topical corticosteroid eye drops
– Contaminated eye drops or lens care solutions
– Swimming or showering while wearing contact lenses
– Systemic diseases that affect immunity (such as diabetes or immunodeficiency)
Read also: Keratoconus Treatment 2023 | Corneal Treatment at Batal Eye Clinic
Treatment of Bacterial Infectious Keratitis
Immediate initiation of antimicrobial therapy is the most appropriate approach. Current guidelines from both the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) recommend broad-spectrum topical antimicrobial agents as first-line treatment for suspected bacterial corneal ulcers.
Antibacterial eye drops are usually effective against most forms of bacterial keratitis. Severe infections may require fortified topical antibiotic preparations that are not commercially available and must be specially compounded. In general, systemic (oral) antibiotics are not necessary for uncomplicated bacterial keratitis. In some cases, a corneal specialist may need to perform additional tests at the cellular or microbiological level to accurately identify the causative organism and tailor therapy.
Read also: Requirements for Vision Correction Surgery | Are You a Good Candidate?

Regardless of the type of eye disease or defect, this is a delicate medical condition that requires a thorough examination and appropriate treatment by a skilled, experienced ophthalmologist, using effective medical tools and technologies to achieve the best possible outcome. Whatever eye condition you are dealing with, you can book an appointment at Batal Specialized Complex to undergo the necessary evaluation and begin addressing your eye problems, no matter how complex they may be.





