Med info
Stye (Hordeolum): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
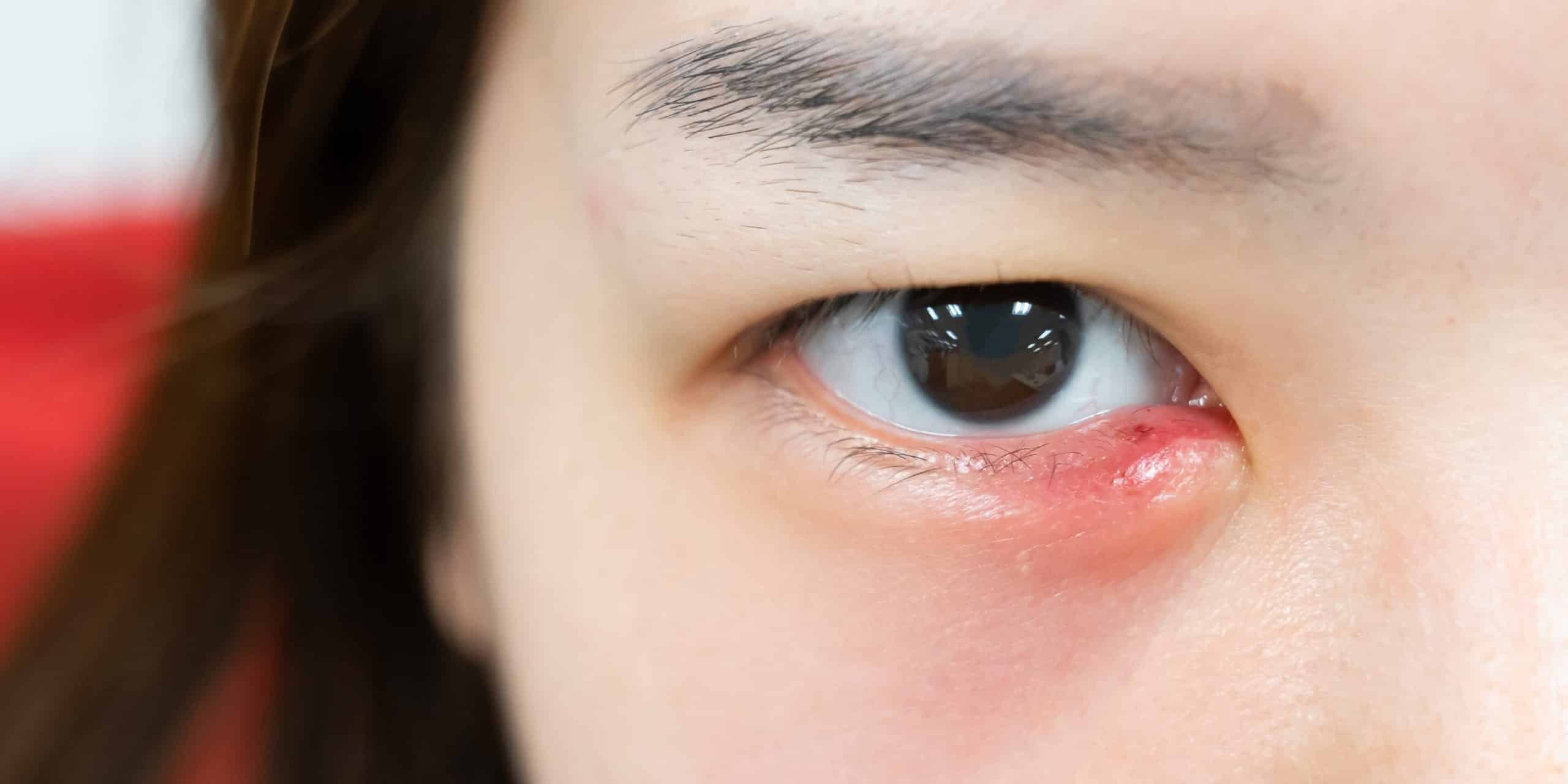
Most bumps that appear on the eyelid are styes (hordeola). A stye is an inflamed oil gland on the edge of your eyelid where the eyelashes meet the lid. It appears as a red, swollen bump that looks like a pimple and is often tender to the touch. This article explains everything related to the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of a stye (شحاذ العين أو جنجل العين).
Also read: Eye Freckles | Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Causes of a Stye
A stye (hordeolum) develops when one of the oil (meibomian) glands in the eyelid becomes blocked. This allows bacteria to grow inside the blocked gland. The process is very similar to the formation of common acne pimples elsewhere on the skin. You may have more than one stye at the same time.
Styes usually develop over a few days and may drain and heal on their own. A stye can also turn into a chalazion, which occurs when the inflamed oil gland becomes completely blocked. If the chalazion becomes large enough, it may start to interfere with your vision.
The condition can be made worse by the presence of Demodex, a common mite that lives on human skin. Demodex has been identified as a cause of blepharitis (eyelid inflammation), and if you have blepharitis, you are more likely to develop styes. Other common types of eyelid lumps include:
Also read: Eyelid Bump | Risk Factors and Treatment
Symptoms of a Stye (Hordeolum)
In addition to a red, swollen bump on the eyelid, other possible symptoms of a stye may include:
Also read: Information About Laser Vision Correction Surgery
Treatment of a Stye
To treat eyelid bumps at home:
Styes often improve on their own without specific treatment. However, they can recur. If you also have blepharitis, treating it may help prevent styes from coming back. With simple measures, the outcome is almost always excellent.
In some cases, the infection can spread to the rest of the eyelid. This is called preseptal (periorbital) cellulitis and may require oral antibiotics. It can resemble orbital cellulitis, which is a more serious condition, especially in children.
Also read: Symptoms of Low Vision and Everything You Need to Know About This Condition
When Should You See an Ophthalmologist?
If you develop a stye, you should contact an eye specialist (ophthalmologist) in the following situations:
Also read: Corneal Transplant Surgery and Everything You Need to Know About This Procedure
To help prevent styes, always wash your hands thoroughly before touching the skin around your eyes. If you are prone to styes or blepharitis, carefully cleaning the eyelid margins to remove excess oil may help. To do this, use a solution of warm water and tear‑free baby shampoo.
Taking oral fish oil supplements may help reduce blockage of the oil glands. Treatment for Demodex infestation may also be beneficial. An eye drop specifically for this condition is expected to be available in the near future. Your ophthalmologist may also recommend using tea tree oil–based products on the eyelids for Demodex.
Also read: Can I Have LASIK if I Have Thin Corneas?

Whatever corneal defects or problems you may have, these delicate eye conditions require careful examination and appropriate treatment by a skilled, experienced ophthalmologist using effective medical tools to achieve the best possible outcome. Whatever eye disease you are dealing with, you can book an appointment at Batal Specialist Complex to undergo a thorough eye examination and start addressing your vision problems, whatever they may be.





