Med info
Hashimoto’s Disease | Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
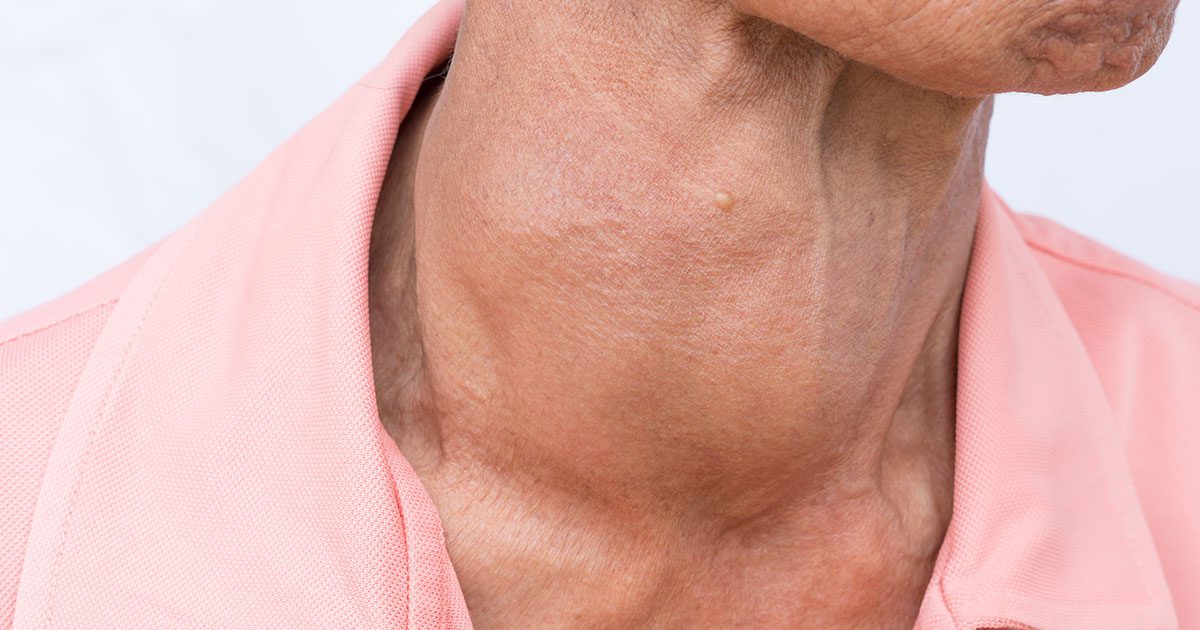
Hashimoto’s disease can lead to hypothyroidism when the thyroid gland is damaged and gradually stops making enough hormones to keep the body working properly. Hashimoto’s is more common in middle‑aged women than in men and can cause fatigue and weight gain.
What Is Hashimoto’s Disease?
Hashimoto’s Disease | Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s disease affects the thyroid gland. It is also called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, or autoimmune thyroiditis.
The thyroid gland makes hormones that essentially control all metabolic functions in the body—that is, how your body converts food into energy and keeps everything running normally.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder in which your immune system no longer recognizes the thyroid as “self” and starts attacking it. Hashimoto’s is common and affects about 5 out of every 100 people in the United States.
Read also: What Is Conductive Keratoplasty?
What Is Hypothyroidism?
In Hashimoto’s, hypothyroidism develops when the thyroid gland can no longer produce enough thyroid hormone to meet the body’s needs because it has been damaged by the immune system. Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism—the process by which your body turns food into energy. Without enough energy, your body cannot function normally and many body systems begin to slow down.
Read also: Endoscopic Orbital Decompression Surgery – Everything You Need to Know
How Does Hypothyroidism Affect Your Body?
Hypothyroidism can affect you both physically and emotionally. For example:
(The original text introduces this heading but does not list examples.
You can insert the symptom list here if you have it, or leave as is.)
Who Is at Higher Risk for Hashimoto’s Disease?
Hashimoto’s disease is more common in women than in men and tends to appear most often between the ages of 30 and 50. It also tends to run in families.
People are more likely to develop Hashimoto’s if they have other autoimmune conditions, such as certain liver diseases, vitamin B12 deficiency (pernicious anemia), gluten sensitivity or celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, lupus, or Addison’s disease.
What Causes Hashimoto’s Disease?
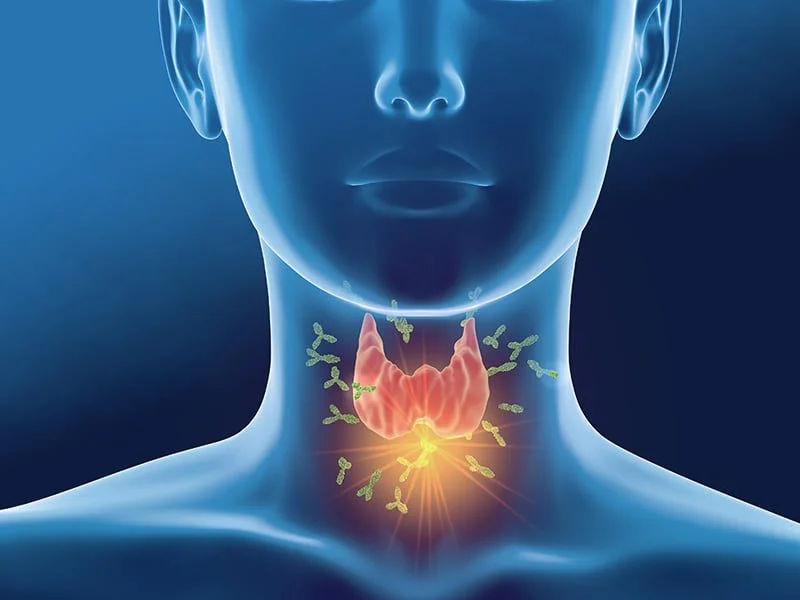
Hashimoto’s is an autoimmune disease, which means the body’s immune system attacks its own cells and organs. Normally, the immune system protects the body from infections caused by bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances.
In Hashimoto’s disease, however, the immune system produces antibodies that attack and damage thyroid tissue. As a result, the thyroid becomes inflamed and gradually loses its ability to produce enough thyroid hormone, eventually leading to hypothyroidism.
Read also: Everything You Need to Know About Pterygium Surgery
Symptoms of Hashimoto’s Disease
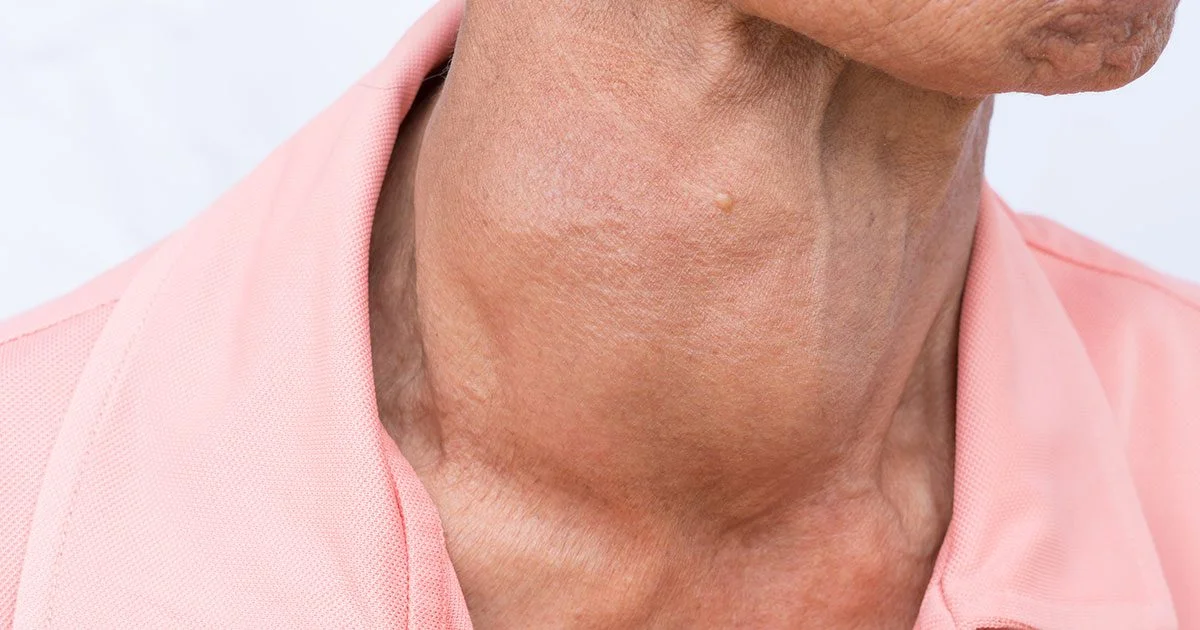
Some people have no symptoms at first. As the disease slowly progresses, the thyroid gland may become enlarged; this is called a goiter, and it is often the first noticeable sign.
A goiter is usually not painful, but it can cause a feeling of fullness in the throat and make the front of your neck look swollen.
Other symptoms of Hashimoto’s disease that may develop over time include:
Again, the Arabic text indicates a list but doesn’t provide it.
Common symptoms (for later addition) include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, dry skin, etc.
How Is Hashimoto’s Disease Diagnosed?
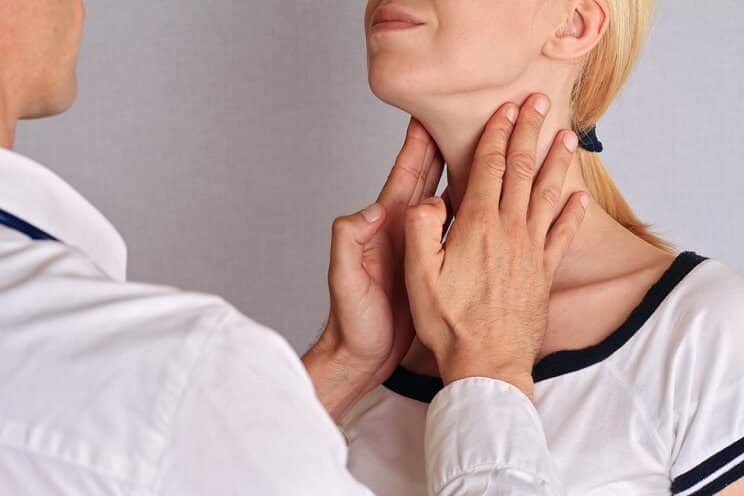
Your doctor will first take a detailed medical history and perform a physical exam. They will feel your neck to check whether the thyroid is enlarged. Blood tests are then ordered and typically include:
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test
A high TSH level usually indicates that the thyroid is not producing enough thyroxine (T4). This finding is consistent with hypothyroidism or subclinical hypothyroidism.
Free T4 Test
A low free T4 level indicates that the person has hypothyroidism.
Thyroid Antibody Test
The presence of thyroid antibodies indicates a higher risk of developing Hashimoto‑related hypothyroidism. The most commonly ordered imaging test is a thyroid ultrasound.
An ultrasound scan shows the size and appearance of the thyroid gland and whether there are any nodules or other growths in the neck area.
Read also: Entropion Repair – Definition, Types, Treatment, and Causes
Does Hashimoto’s Disease Always Need Treatment?
Does Hashimoto’s Disease Always Need Treatment?
Not everyone with Hashimoto’s disease develops hypothyroidism. Because elevated thyroid antibody levels in Hashimoto’s are associated with an increased risk of hypothyroidism, endocrinologists typically choose to monitor your condition and watch for any changes in thyroid function over time.
Treatment for Hashimoto’s Disease
If Hashimoto’s disease progresses to hypothyroidism, the standard treatment is a synthetic (man‑made) form of thyroid hormone called levothyroxine.
This medication restores normal thyroid hormone levels. You will need to take it every day for the rest of your life. You and your doctor will work together to adjust your dose to keep your hypothyroidism well controlled.
Is There a Special Diet for People With Hashimoto’s Disease?
There is no specific “Hashimoto’s diet.” However, certain foods, medications, or supplements can interfere with your body’s ability to absorb levothyroxine.
These include iron and calcium supplements, some ulcer medications, sucralfate, cholestyramine, and aluminum hydroxide (found in some antacids). Taking these products at least four hours before or after your levothyroxine dose can help avoid absorption problems.
Talk to your doctor about any diet‑related questions you have. Eating a healthy diet, staying active, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can all support your immune system and overall health.
Regardless of lifestyle measures, if you have been diagnosed with hypothyroidism, you will need to continue taking your prescribed thyroid medication.

Finally, Batal Specialized Complex in Saudi Arabia is considered one of the most advanced and leading medical centers in the field of eye care and eye disease treatment. The center’s reputation continues to grow day by day thanks to its highly qualified ophthalmologists and its use of the latest technologies for eye diagnosis and treatment. If you are experiencing any eye problems, book an appointment at Batal Specialized Complex to receive the best possible medical advice from an eye specialist at the center.
Read also: Hypothyroidism | Causes, Symptoms, Testing, and Treatment


