Med info
Fundus examination: what is it? How is it performed?
A fundus examination, also called fundoscopy, is a test that allows your doctor to see inside your eyes and properly evaluate your fundus and other structures, with the help of an ophthalmoscope or fundus camera.
Fundus examination allows examination of the retina and is the most reliable method for diagnosing medical conditions and identifying risk factors for possible retinal vision loss. Diabetics should have at least an annual background check after mydriasis with retinal control drops to rule out diabetic retinopathy, the most common cause of blindness worldwide at age under 50.
In addition, it is the primary examination for evaluating both blood vessels and the optic nerve in serious conditions such as glaucoma.
What is fundus examination?
Fundus examination is one of the most common tests in ophthalmology examinations. It is a simple and painless test that gives us complete information about the main structures of the back of the eyeball. The results obtained help us diagnose and monitor various eye diseases, and ultimately determine the best treatment for them.
Ophthalmologists perform the examination using an instrument called an ophthalmoscope, a device that allows the back of the eye to be seen through a light source and lens system.
In most cases, it is necessary to dilate the pupil beforehand using eye drops. For this reason, we recommend bringing someone with you because after the examination, the pupil will continue to dilate and vision will be blurred for a few hours.
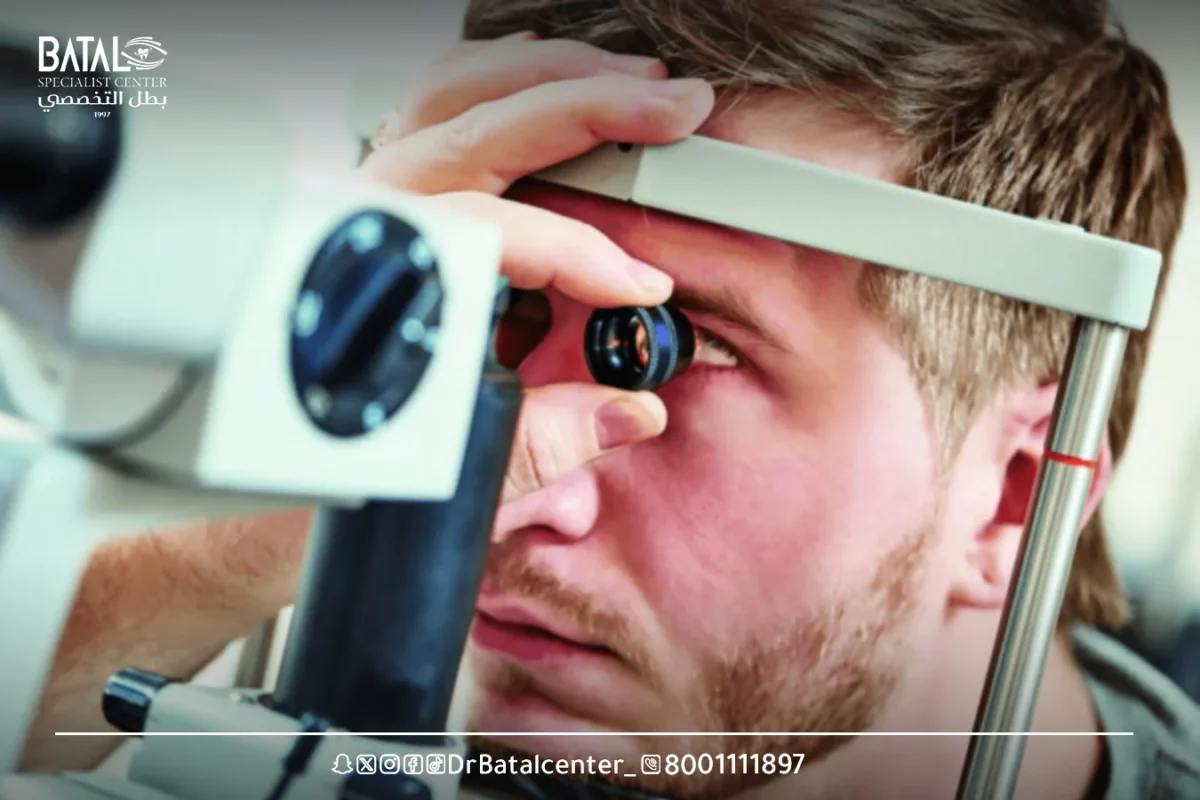

- What is the fundus of the eye?
The fundus is the back of the eye and includes: the optic nerve, macula, vascular arches, peripheral retina and choroid.
- Fundus examination in English
The scientific name for fundoscopic examination in English is Ophthalmoscopy.
What does a fundus examination reveal?
A fundus examination, usually performed by an ophthalmologist, is a common procedure used to image the internal structures of the eyeball, including the vitreous, retina, retinal blood vessels, macula, and optic disc.
This short procedure, which takes 2-5 minutes, is essential in the retinal specialist examination process, and is also used to detect eye diseases and conditions or to evaluate a patient’s symptoms.

The importance of fundus examination and diagnosis of retinal diseases
An ophthalmologist can use a fundus examination to check for eye diseases or other medical conditions, including:
- Vitreous detachment.
- Myopia.
- Retinal detachment.
- Diabetes.
- Suspected tumor.
- Macular diseases.
- Taking certain medications that can cause damage to the macula and optic nerve (hydroxychloroquine, tamoxifen, etc.)
- Blue.
- Retinal vessel occlusion.
- Glass hemorrhage.
- Retinal atrophy.
- Choroidal diseases.
- Infections.
- Traumas.
- Postoperative complications.
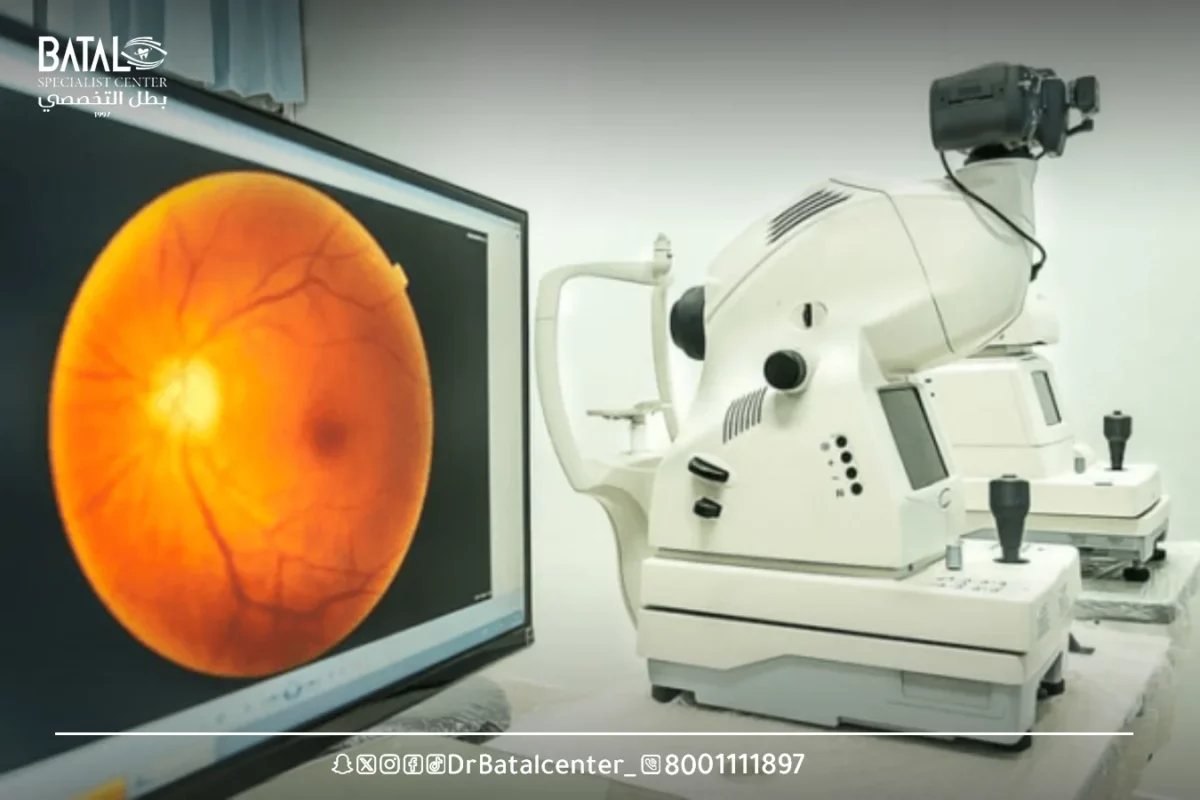
Tools and devices used in fundus examination
Fundus examination is a diagnostic procedure used to examine the internal structures of the eye, including the retina, optic disc, blood vessels, and other important features. Various instruments are used in ophthalmoscopy to assist in this examination. Here are some tools used to examine the fundus:
Fundus examination device
- Ophthalmoscope: An ophthalmoscope is the primary instrument used to examine the eye. It consists of a light source, usually an adjustable beam of white light, and various lenses that allow the examiner to see the internal structures of the eye. The ophthalmoscope may have different settings to adjust the brightness and focus of light.
- Direct ophthalmoscope: A direct ophthalmoscope is a portable instrument that provides an enlarged view of the retina and other structures at the back of the eye. It is equipped with a light source and a lens assembly that allows the examiner to examine the eye directly through the pupil.
- Indirect ophthalmoscope: An indirect ophthalmoscope is a larger instrument that is usually mounted on the examiner’s head or carried by an assistant. It consists of a light source, a condensing lens, and a portable lens placed near the patient’s eye. An indirect ophthalmoscope provides a wider field of view and a more panoramic view of the retina compared to a direct ophthalmoscope.
- Slit lamp biomicroscope: While primarily used to examine the front of the eye, a slit lamp biomicroscope can also be used for ophthalmoscopy. It combines a high-intensity light source with a microscope and allows the examiner to see the retina and other structures in detail.
- Fundus examination drops
Dilated eye drops are commonly used to enlarge the pupil. This allows a better view of the retina and other structures during the examination.
The most commonly used eye drops to dilate the eye during a fundus examination contain medications such as tropicamide, phenylephrine, or cyclopentolate.
These drops are usually given by an eye care professional, and their effect can last for a few hours. It is important to note that the use of eye drops and their specific composition may vary depending on the patient’s condition and the preferences of the healthcare provider.
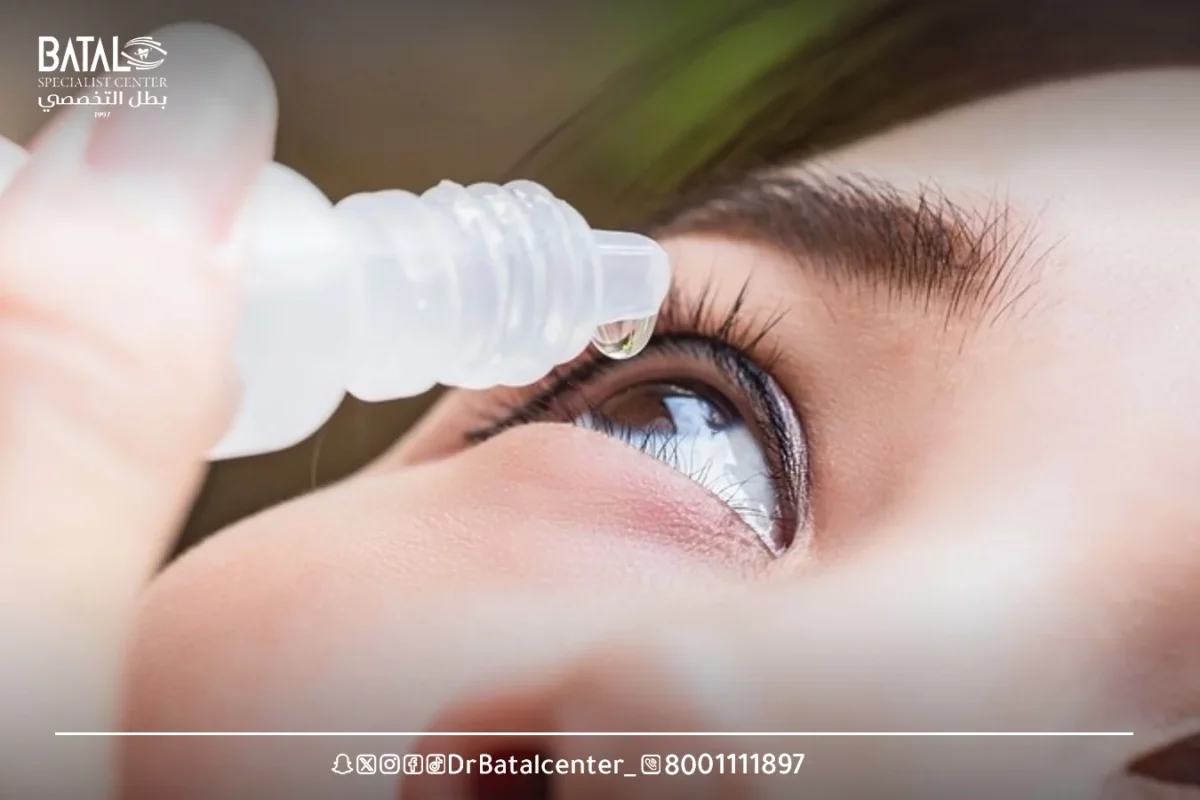
Fundus examination drops and their role in dilating the pupil
After applying fundus examination drops to dilate the pupil, this involves using special eye drops designed to enlarge the pupil opening and temporarily disable it from closing in response to bright light. A large, dilated pupil allows the doctor to see the “peripheral” parts of the retina and vitreous. There are three steps to fundus examination:
1- Direct fundus examination
- The patient is seated in a dark examination room
- The doctor uses a portable ophthalmoscope to shine bright light onto the eye.
- This instrument, which is the size of a thin flashlight, uses several small lenses that focus on the internal structures of the eye and display the image back to the examiner.
2- Indirect fundus examination
- This is usually done with the patient lying in the examination chair.
- The doctor keeps his eyes open while wearing a fundus examination instrument on his head.
- The doctor shines light on this lamp through a lens that he holds in front of the eye.
- This lens magnifies the image that the doctor sees through the mirrors and special lenses attached to the fundus examination device.
- The patient is asked to look in different directions to reach the area to be examined
- The doctor may use a method in which slight pressure is applied to the side of the eye using a special instrument, a technique that gives the doctor a better view of the distal peripheral areas on the retina.
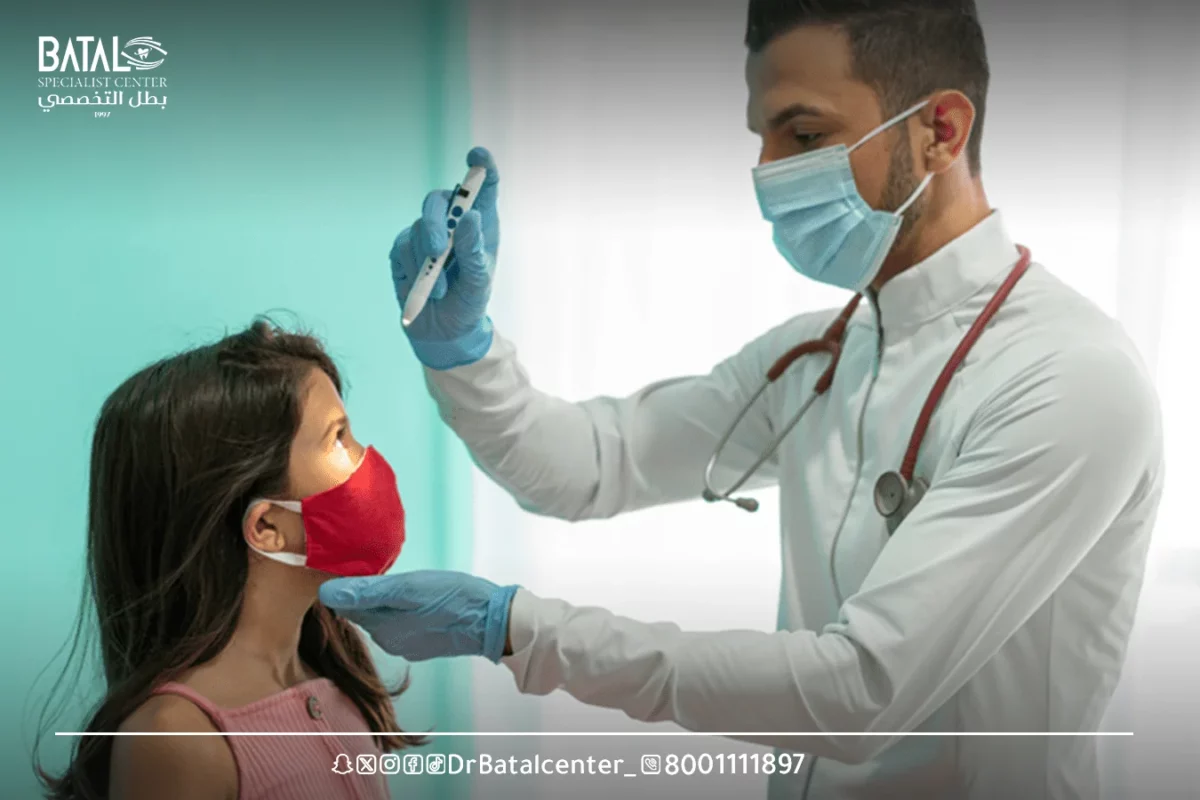

3- Examination of the fundus of the eye with a slit lamp
This is the most commonly used type of fundus examination because the patient is usually already sitting in front of the slit lamp, an eye microscope that allows the doctor to see many areas of the eyeball at different magnifications.
- The patient sits upright in the examination chair in front of the slit lamp with his chin on a support to keep his head stable.
- The doctor holds a small magnifying glass in front of the eye and illuminates the slit lamp light source through it.
- The enlarged image is reflected into the eye through the lens and viewed by the doctor through a slit lamp scope.
- The doctor has the option to increase or decrease the magnification using this method.
Fundus examination results: normal and abnormal
Fundus examination results can provide valuable information about the health and condition of structures inside the eye. The specific results and their significance will depend on the purpose of the examination and the presence of any specific eye conditions or abnormalities. Here are some possible findings that may be observed during the examination:
1- Normal results: On a normal fundus examination, the optic disc, macula, blood vessels and other structures will appear healthy and without any signs of disease or deformities. This indicates good eye health.
2- Abnormal results: The abnormalities observed during ophthalmoscopy can vary greatly and may include:
- Optic disc abnormalities: These can include swelling of the optic disc (papillary edema), cupping of the optic disc (indicating glaucoma), pallor of the optic disc (loss of nerve fibers), or other optic nerve abnormalities.
- Retinal abnormalities: These may include retinal tears, detachment, bleeding, discharge (an indicator of diabetic retinopathy), or other signs of retinal disease.
- Vascular changes: A fundus examination can reveal abnormalities in the blood vessels, such as stenosis, tortuosity, or signs of blood vessel leakage (which appear in conditions such as hypertensive retinopathy or retinal vein occlusion).
- Macular abnormalities: Ophthalmoscopy can detect macular edema, macular holes, or other problems related to the macula.
- Presence of tumors: Ophthalmoscopy may identify abnormal growths or tumors in the eye, such as retinoblastoma or choroidal melanoma.

Post-fundus examination: important recommendations and tips
After receiving the results of a fundus examination, it is important to follow the ophthalmologist’s recommendations. These recommendations may include:
- If any eye abnormalities or conditions are detected, ophthalmologists will discuss the appropriate treatment plan. This may include medication, surgery, laser therapy, or other interventions, depending on the specific diagnosis.
- Regular follow-up visits may be necessary to monitor the condition or the development of any eye abnormalities or conditions identified during the examination.
- Your eye care professional may make recommendations for lifestyle modifications to improve eye health, such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet, managing systemic conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure, or using goggles when necessary.
- If any medications are prescribed, it is important to follow the prescribed dosage and schedule carefully.
- You should be aware of any new or worsening symptoms and report them immediately to your eye care professional.
Places to perform fundus examination
Routine fundus examinations are performed in an ophthalmologist’s office or clinic during the examination. Ophthalmologists are specialized eye care physicians with extensive training in the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases. They also have access to a wide range of ophthalmic instruments, including ophthalmoscopes, slit-lamp biomicroscopes, and other necessary equipment.
Fundus examination at Batal Specialized Complex in Jeddah
At Batal Specialized Complex in Jeddah, fundus examination can be performed in specialized departments within the complex, which are equipped with advanced diagnostic and treatment facilities.
Ophthalmologists at Batal Specialist Complex in Jeddah may perform fundus examinations for more complex cases or when additional investigations or consultations are needed.
These clinics within Batal Specialist Complex in Jeddah may offer a wide range of services, from routine eye examinations to specialized treatments and surgeries.
Approximate fundus examination price
The cost of a fundus examination can vary depending on several factors, including location, health care provider, and additional tests or procedures involved.
In general, the price of a basic fundus examination without any additional tests or procedures can range from SAR 200 to SAR 750. However, this is a rough estimate, and the actual cost may be higher or lower based on the factors mentioned above.
Additional diagnostic tests or imaging techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT), fluorescein angiography, or visual field testing may be required, as this may incur additional costs. Prices for these specialized tests can vary greatly depending on their complexity and the equipment used.
Furthermore, the cost may also be affected by factors such as insurance coverage and the type of healthcare provider (private clinic, or hospital.
Additional information for fundus examination
Here is some additional information for fundus examination:
- Fundus examination for children
Children may have a fundus examination to evaluate their eye health and detect any abnormalities. However, examining children may require special techniques and considerations to ensure their cooperation and comfort during the procedure. A pediatric ophthalmologist in Jeddah with experience working with children is best suited to perform an eye examination.
- Fundus examination of infants and newborns
Fundus examination can be difficult in infants and newborns due to their small size and inability to cooperate. Indirect ophthalmoscopy is commonly used for this age group, often using specialized lenses and portable equipment. It helps evaluate the retina, optic nerve, and other important structures in infants’ eyes to detect any birth defects, retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), or other conditions.
Fundus examination for premature babies
Premature babies are at risk of developing retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), a condition that can threaten vision. Ophthalmoscopy is an essential tool for examining and monitoring retinopathy of prematurity in premature infants. Screening frequency and screening protocols for retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) are determined by guidelines developed by pediatric ophthalmologists and neonatologists.
Fundus examination for diabetics
Individuals with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, a condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina. Fundus examination for diabetics is crucial to detecting and monitoring diabetic retinopathy. Regular fundus examinations are recommended for diabetics to identify any changes in the retina and initiate appropriate treatment to prevent vision loss.
Fundus and brain examination
A fundus examination can provide insight into the health of blood vessels and other structures in the eye that are closely related to the brain. Certain conditions, such as increased intracranial pressure or papillary edema, can be detected by ophthalmoscopy. Swelling of the optic disc or other abnormalities observed during examination may indicate underlying brain conditions that require further investigation and management.
Fundus examination and headache
Fundus examination is not usually used as the primary diagnostic tool for headache. However, if the headache is accompanied by certain visual symptoms or signs of increased intracranial pressure, an ophthalmoscopic examination may be performed to evaluate the optic disc and rule out any underlying causes.
Harmful effects of fundus examination drops
Eye drops used to dilate the pupil during ophthalmoscopy can cause temporary side effects such as blurred vision, increased sensitivity to light, and difficulty focusing on nearby objects. These effects usually subside within a few hours.
In rare cases, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to eye drops. It is important to follow the instructions given by your eye care professional and report any unusual or severe side effects.
Fundus examination under anesthesia (in specific cases)
In certain cases, such as uncooperative patients (including infants or young children), individuals with severe disabilities, or those who require intensive examination or treatment, a fundus examination may be performed under anesthesia. This ensures patient comfort and allows a comprehensive examination or procedure to be performed safely.
Prepare for a thorough retinal examination with experts from Batal Specialized Complex in Jeddah
At Batal Specialized Eye Complex in Jeddah, we give your eyes the care they deserve through precise examinations that include examining the fundus of the eye with the latest medical devices and international technologies.
Our specialist doctors perform this examination for early detection of retinal and optic nerve diseases, allowing rapid intervention before any complications develop that may affect vision.
Whether you’re diabetic, have poor vision, or just want to check on the health of your eyes — we’re here to give you clearer vision and a safer life.
Book your examination appointment today at Batal Specialized Complex, and get ready to see the smallest details with a new eye.



