Med info
Eye Swelling Treatment
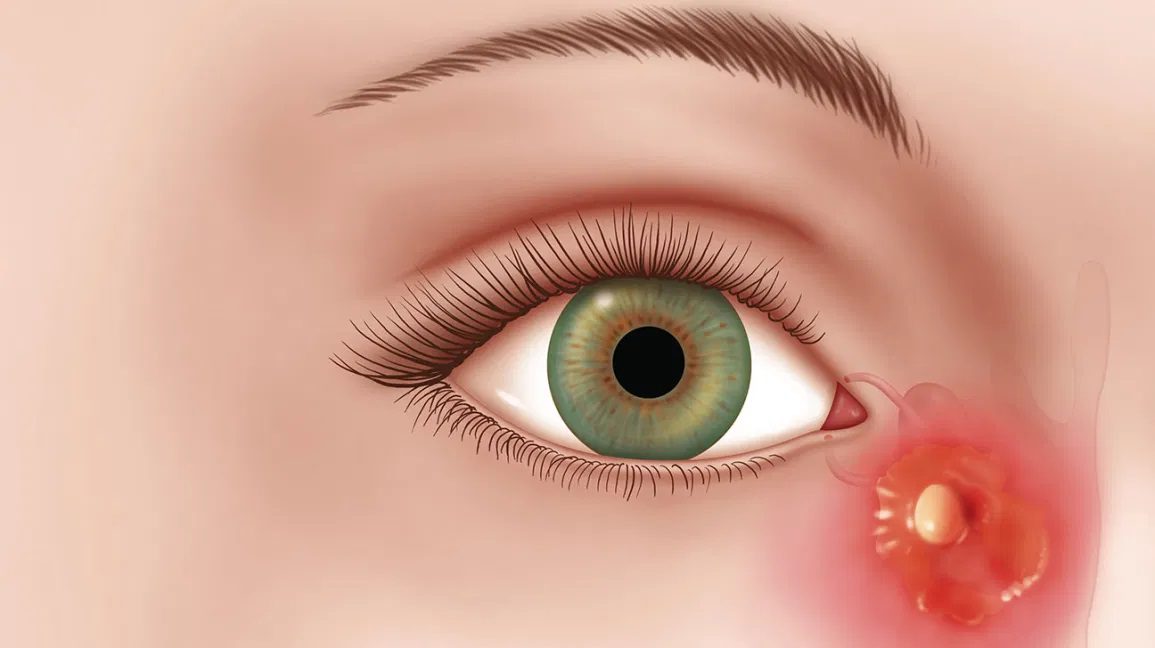
Eye swelling is the enlargement of the upper or lower eyelids, or both, in one or both eyes. It occurs due to fluid buildup or inflammation of the delicate tissues around the eye. A wide range of diseases, disorders, and conditions—from mild to severe—can lead to swollen eyes. Swelling may result from harmless causes such as crying or rubbing the eyes, or from more serious problems like infections, trauma, or cancer.
The most common cause of eye swelling is allergy, either through direct contact with an allergen (such as pet dander that gets into the eyes) or through a systemic allergic reaction (such as a food allergy). Swelling can be short-lived and resolve quickly, as in a mild allergic reaction to pet dander or dust. However, eye swelling that develops gradually and appears along with other symptoms can signal a more serious condition affecting the whole body, such as hyperthyroidism (Graves’ disease) or an infection.
Because eye swelling (edema) can be a sign of a serious condition, it is important to discuss your symptoms with a doctor. If eye swelling is accompanied by fever, vision problems (such as blurred vision), abnormal or limited eye movements, eye protrusion (bulging), or signs of anaphylaxis (swelling of the tongue and throat, difficulty breathing), you should visit the Eye Center at Al-Batal Specialized Hospital in Jeddah, which is known for providing urgent medical care.
Read also: Causes of Yellow Eyes, Treatment, and Indications
What Other Symptoms Can Occur with Eye Swelling?
Eye swelling may occur along with other symptoms depending on the underlying disease, disorder, or condition. Swollen eyes often appear after facial injuries or surgery. For example, a broken nose can cause bruising and puffy eyes. There may be problems in the eye itself, or symptoms may affect other body systems, such as the immune system.
Eye swelling along with a wide range of other symptoms—such as increased appetite, heat intolerance, and fatigue—can point to an autoimmune disorder called Graves’ disease. Swelling due to generalized edema may be associated with swelling in the face and possibly the legs. Swelling caused by infection may include redness, fever, pain, and sometimes difficulty moving the eyeball.
Vision Changes and Other Eye-Related Symptoms That May Occur with Eye Swelling
Eye swelling may be accompanied by visual disturbances and other eye symptoms, including:
Other Symptoms That May Occur with Eye Swelling
Eye swelling may also be accompanied by other abnormal signs and symptoms, including:
Serious Symptoms That May Indicate a Life-Threatening Condition
In some cases, eye swelling can signal a serious or life-threatening condition that must be evaluated immediately in an emergency setting. Life‑threatening symptoms include:
What Causes Eye Swelling?
Although eye swelling can result from relatively mild conditions, such as a blocked meibomian (oil) gland, it can also be caused by serious or life‑threatening problems, such as anaphylactic shock, which must be evaluated immediately in the emergency department.
Common Causes of Eye Swelling
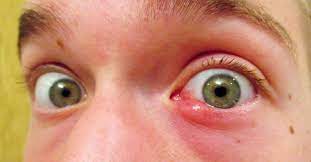
Other Causes of Eye Swelling
Eye swelling can be caused by a variety of infections, including:
Eye swelling can also be a symptom of several other conditions, including:
Prevention of Eye Swelling
Preventing eye swelling depends on its underlying cause:
How Is Eye Swelling Treated?
Most cases of eye swelling can be managed with simple home remedies, such as cold compresses for occasional redness and puffiness. However, you should see a doctor right away if eyelid swelling is chronic, very severe, or associated with other symptoms or changes in vision. Medical treatments may include:
Home Treatment for Eye Swelling
For mild eyelid swelling, the following home remedies may be helpful:
How to Treat Eye Swelling Caused by Allergies
For eye swelling related to allergies—such as seasonal allergies or pet allergies—you can try the following over‑the‑counter home treatments:
For eye swelling associated with severe allergic reactions, you should consult an eye specialist immediately.
How Long Does It Take for Eye Swelling to Go Down?
For temporary causes—such as allergies—eye swelling may take a few hours to improve with home remedies and antihistamines. For minor infections and blocked glands, swelling usually decreases within one to three weeks with appropriate treatment. Swelling caused by cellulitis or orbital cellulitis may take longer to resolve, especially if the infection does not respond well to antibiotics and additional therapy is required.
For generalized edema and “puffy” eyes, the time needed for swelling to subside depends on the underlying diagnosis and treatment. For example, temporary fluid retention from eating a salty meal may resolve within about 24 hours with home management (increasing water intake and reducing salt). For more serious causes of eye swelling, such as thyroid disorders, the swelling may not improve until the underlying problem is properly treated.
When Should You See a Doctor for Eye Swelling?
In some situations, eye swelling is a symptom of a serious condition that should be evaluated immediately by a healthcare professional, or at the Eye Center at Al‑Batal Specialized Hospital in Jeddah. Life‑threatening warning signs include:
What Are the Possible Complications of Eye Swelling?

Complications related to eye swelling can develop gradually and vary depending on the underlying cause. Because eye swelling can result from serious diseases, failing to seek timely care may lead to complications and permanent damage. It is therefore important to visit the Eye Center at Al‑Batal Specialized Hospital in Jeddah if you experience any type of persistent swelling or other unusual eye symptoms. Once the underlying cause is diagnosed, following the treatment plan prescribed by your doctor can help reduce potential complications, including:
Read also: Top 10 Symptoms of Myopia and How to Treat It


