Med info
Gingivitis Treatment
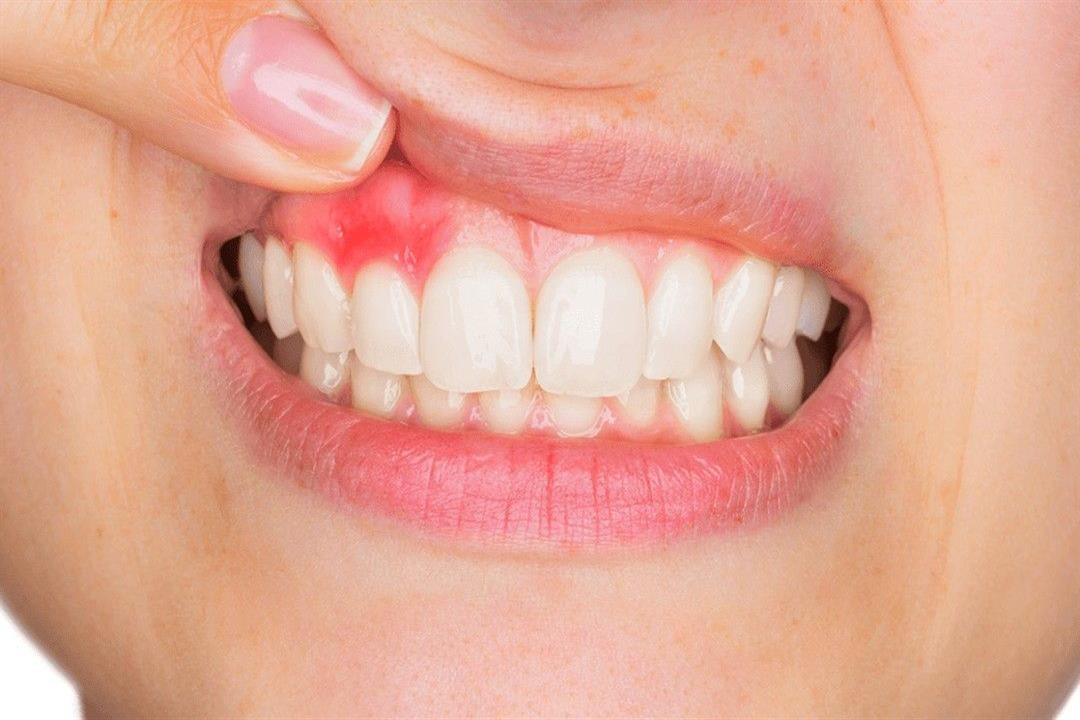
Gingivitis (inflammation of the gums around the teeth) is the most common form of periodontal disease (diseases affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth). When gingivitis becomes chronic, it can lead to gum recession, and it is classified according to severity, ranging from mild to severe gum inflammation.
Although bacteria normally live in our bodies and often provide protective benefits, they can also be harmful. The mouth is an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive: it is warm, moist, and has a constant supply of food. If the immune system is not functioning properly, bacteria can multiply rapidly in the mouth.
Infection begins when the body’s immune system is stressed or weakened. Gingivitis is an infection that occurs when bacteria invade the soft tissues and bone surrounding the teeth. The severity of this infection can range from mild to severe and may sometimes be a sign of an underlying, potentially life‑threatening systemic disease.
Also read: Dental filling prices in Jeddah and types of dental fillings
Causes and Risk Factors of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a bacterial infection that affects the gums, and there are several reasons and risk factors that contribute to its development:
[Content continues here in the original article.]
Signs and Symptoms of Gingivitis
[Content continues here in the original article.]
How Is Gingivitis Treated?
For mild gingivitis, good oral hygiene at home is usually enough. This includes brushing and flossing regularly and correctly. Routine dental checkups and professional cleanings are typically all that is needed to treat and prevent gingivitis.
One possible complication of gingivitis is the development of ulcers on the gums. If these ulcers are widespread, this may be a sign of acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG), which requires proper diagnosis and medical treatment. In such cases, you should visit the dental clinic at Al Batal Specialized Complex in Jeddah, where modern dental technologies and specialists in periodontology and gum disease are available.
Also read: My experience with immediate dental implants
Getting Rid of Gingivitis
Early or acute gingivitis is treated with a thorough professional dental cleaning performed by a dental hygienist, along with diagnosis and follow‑up by a dentist. In cases where gingivitis has become chronic or has been diagnosed as acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG), referral to a periodontist (gum specialist) may be necessary to help manage and treat the condition.
Diagnosis of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a clinical diagnosis, which means the dentist can usually identify it by taking a detailed medical and dental history and performing a comprehensive oral examination. Blood tests, dental X‑rays, or tissue samples may be requested for patients who do not respond to initial treatment. In all cases, the patient should be evaluated for any underlying systemic disease that might be contributing to the gum inflammation.
Also read: Types of dental braces with pictures and their prices
Home Treatment for Gingivitis
The following home‑care measures can help treat and control gingivitis:
[Content continues here in the original article.]
Also read: Types of dental fillings
Conclusion
Most cases of mild gingivitis can be managed effectively with proper oral hygiene and regular dental visits. In more severe gum disease, gum recession may be significant enough to require surgical correction.

It is important to understand that gingivitis results primarily from an individual’s oral hygiene and is not considered a contagious condition. Therefore, controlling personal risk factors will greatly improve the prognosis and treatment outcome. For proper evaluation, monitoring, and management of gum disease, you should visit the dental center at Al Batal Specialized Complex in Jeddah.


