Med info
Graves’ Disease | Everything You Need to Know About the Most Common Cause of Hyperthyroidism

Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the thyroid gland, causing it to produce excessive amounts of thyroid hormone — a condition known as hyperthyroidism. Thyroid hormones regulate body temperature, heart rate, and metabolism.
Hyperthyroidism can lead to problems in organs such as the heart, as well as in the bones and muscles. Fortunately, several treatment options are available.
What Is Graves’ Disease?
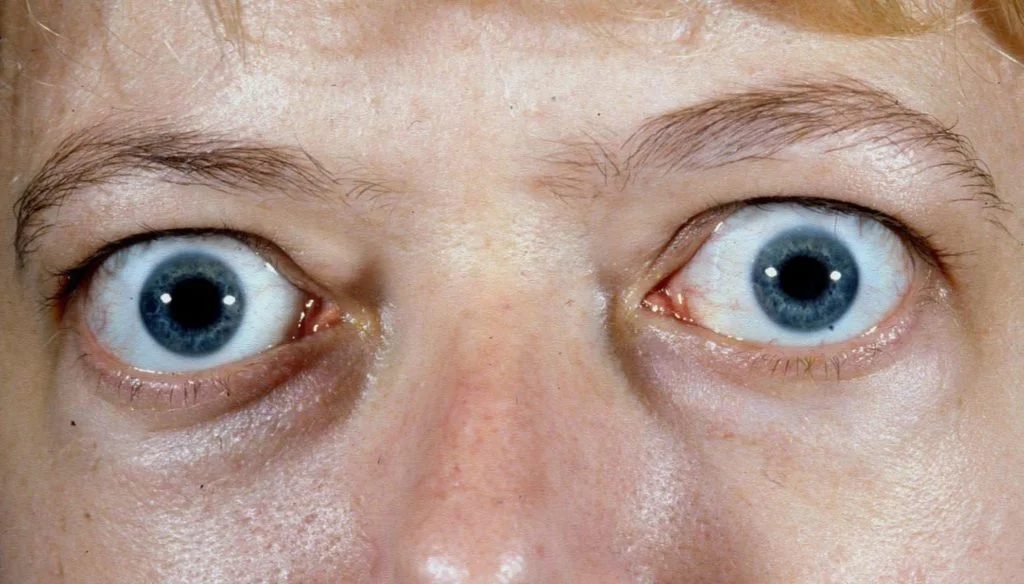
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in the thyroid gland for unknown reasons. It is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid produces too much thyroid hormone.
The thyroid is a small, butterfly‑shaped endocrine gland located at the front of your neck just under the skin. Its main role is to regulate the speed of your metabolism — how your body converts the food you eat into energy — by releasing specific hormones.
The disease is named after Robert Graves, an Irish physician who first described the condition in the 19th century.
Read also: Before and After Eye Treatment Photos
Who Does Graves’ Disease Affect?
Graves’ disease is more common in people assigned female at birth than in those assigned male at birth. It most often appears between the ages of 30 and 50, but it can also affect children and older adults.
Your risk of developing Graves’ disease increases if you have a family history of thyroid disease or if you smoke cigarettes. You are also more likely to develop Graves’ disease if you have another autoimmune disorder, such as:
How Common Is Graves’ Disease?
Although Graves’ disease is the most frequent cause of hyperthyroidism, accounting for about 60% to 80% of all hyperthyroidism cases, it is still relatively uncommon overall. Approximately 1.2% of people in the United States have hyperthyroidism.
Read also: Eyelid Lift Surgery | The Complete Guide from Batal Specialized Center
How Does Graves’ Disease Affect My Body?

Thyroid hormone affects many organs and body functions. Because of this, Graves’ disease and the resulting hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormone) can impact many parts of your body, including:
For example, excess thyroid hormone can cause a rapid heart rate and contribute to more serious heart conditions. It can also lead to osteoporosis (bone thinning and weakness). Since Graves’ disease can influence so many aspects of your health, it’s important to seek medical care.
What Are the Symptoms of Graves’ Disease?
Symptoms of Graves’ disease usually develop gradually and may take several weeks or months to become noticeable. Graves’ disease causes hyperthyroidism, which speeds up certain body functions. There are many possible symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
You may experience just a few of these symptoms or several of them at the same time. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism can include:
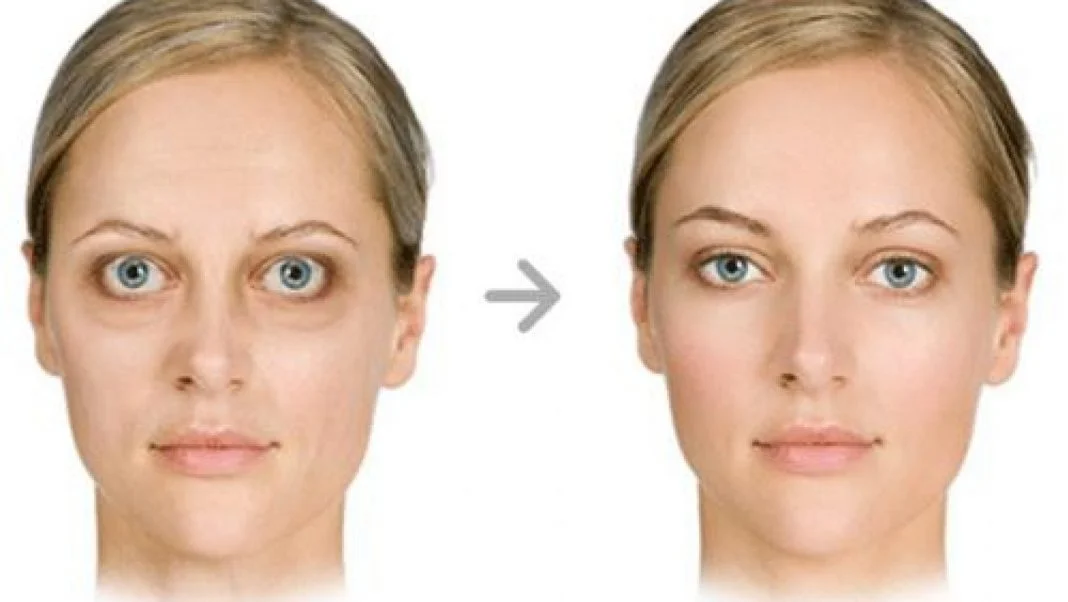
If you have these symptoms, you should see your healthcare provider. Graves’ disease can also cause eye-related symptoms, including:
This condition is called Graves’ ophthalmopathy, thyroid eye disease, or Graves’ eye disease. Only about one‑third of people with Graves’ disease develop this complication. If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to see an ophthalmologist.
In addition, a minority of people with Graves’ disease develop thickened, reddish, bumpy skin over the shins known as pretibial myxedema, or Graves’ dermopathy. It is usually mild and painless, though it can be uncomfortable for some individuals.
Read also: Age Calculator and How Aging Affects the Eyes
What Causes Graves’ Disease?
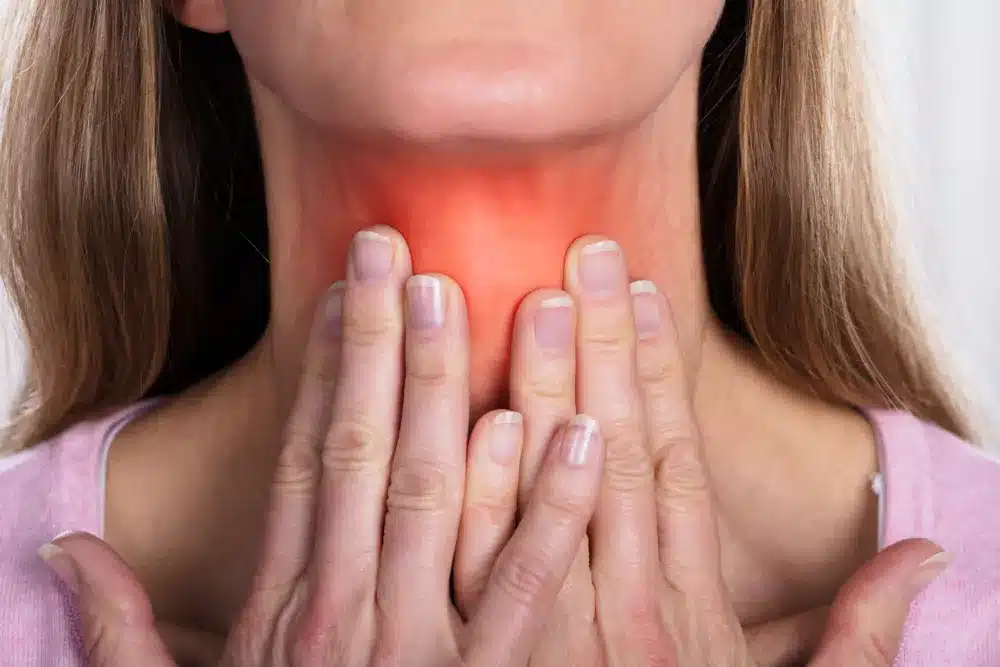
Researchers do not fully understand what triggers autoimmune diseases like Graves’ disease. For reasons that are not entirely clear, the immune system begins producing an antibody called thyroid‑stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI). TSI attaches to healthy thyroid cells and stimulates the thyroid to release excessive amounts of thyroid hormones.
This autoimmune attack is likely driven by a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental factors, such as:
How Is Graves’ Disease Diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history, including any family history of thyroid disease, and will perform a physical examination. They may also order the following tests to confirm a diagnosis of Graves’ disease:
Thyroid Blood Tests
These blood tests measure the level of thyroid hormones in your blood as well as thyroid‑stimulating hormone (TSH). A low TSH level indicates that the thyroid is producing too much hormone. When thyroid hormone levels are high, the pituitary gland responds by lowering its production of TSH.
Thyroid Antibody Tests
These tests help distinguish between different autoimmune thyroid diseases. In Graves’ disease, the main associated antibodies are:
– TSI (thyroid‑stimulating immunoglobulins)
– TBII / TBI (thyrotropin‑binding inhibitory immunoglobulins)
Radioactive Iodine Uptake and Thyroid Scan
In this test, you swallow a small amount of radioactive iodine. Your provider then measures how much of this iodine your thyroid gland absorbs. A high radioactive iodine uptake is a typical finding in Graves’ disease.
Doppler Ultrasound (Thyroid Blood Flow Study)
This test uses sound waves to detect increased blood flow within the thyroid gland, which is often seen in Graves’ disease. Your provider may order this test if radioactive iodine uptake is not appropriate for you, such as during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Graves’ Disease and Pregnancy

Thyroid hormones are essential for the development of the baby’s brain and nervous system. If hyperthyroidism and Graves’ disease are not properly treated during pregnancy, they can pose risks to both you and your fetus.
Your doctor may check your thyroid hormone levels monthly during pregnancy to ensure they stay within a safe range. Overtreatment with thyroid hormone or inadequate control of hyperthyroidism in pregnancy can increase the risk of:

In conclusion, Batal Specialized Center in Saudi Arabia is considered one of the leading and most advanced medical centers in the field of eye care and eye disease treatment. The center’s reputation continues to grow thanks to its highly qualified ophthalmologists and its use of the latest diagnostic and therapeutic eye technologies. If you are experiencing any eye problem, book an appointment at Batal Specialized Center to receive the best ophthalmic consultation and care from a specialized eye doctor.
Read also: What Do You Know About Eye Ointment?





