Glaucoma (Blue Water)
Glaucoma is a condition in which intraocular pressure (IOP) rises and gradually reduces blood flow to the optic nerve. Over time, this damage can lead to permanent vision loss and, in severe cases, blindness.
Book an Appointment or Medical Consultation
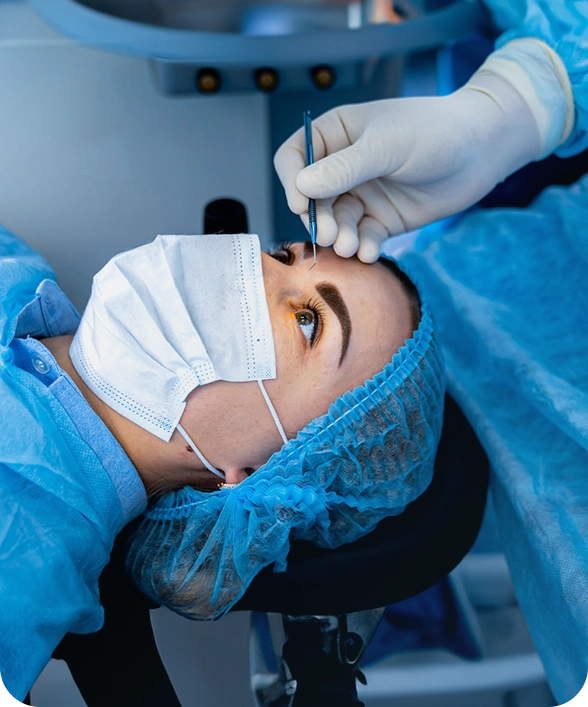
Glaucoma Surgery at Batal Eye Specialty Center – Jeddah
Glaucoma is a condition in which intraocular pressure (IOP) rises and gradually reduces blood flow to the optic nerve, potentially leading to permanent vision loss. It is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide. In most cases, treatment begins with medications to lower eye pressure. However, when medications are not effective, surgical intervention becomes necessary. The most common surgical procedure for glaucoma is trabeculectomy, followed by the placement of a glaucoma drainage implant if needed. Like most eye surgeries, trabeculectomy is typically a short procedure (usually under 60 minutes) and is performed under monitored anesthesia care with local anesthesia. In some cases, glaucoma drainage procedures may be performed under general anesthesia. During glaucoma surgery, laser technology may be used to open blocked drainage channels, allowing excess fluid to exit the eye and relieve pressure on the optic nerve. Reducing this pressure is essential to prevent further damage to the optic nerve and protect remaining vision.

What Is the Difference Between Cataract and Glaucoma?
Cataract and glaucoma are two completely different eye conditions, both in cause and in effect. Cataract (White Water) occurs due to the buildup of proteins in the natural lens of the eye, causing it to lose its transparency. Symptoms develop gradually and include blurred vision, difficulty seeing at night, and increased sensitivity to light. Cataracts can be effectively treated through surgery by replacing the cloudy lens with an artificial intraocular lens. Glaucoma (Blue Water), on the other hand, damages the optic nerve and usually shows no symptoms in its early stages. As the disease progresses, patients may experience loss of peripheral (side) vision. There is no permanent cure for glaucoma, but it can be controlled with eye drops, laser treatment, or surgery to prevent further vision loss.
The Difference Between Cataract and Glaucoma
Cataract (White Water)
Cataract is caused by clouding of the natural lens of the eye and is the leading cause of blindness worldwide. Vision can be effectively restored through surgery. In most cases, delaying cataract surgery does not cause serious harm. However, leaving it untreated for too long can make the procedure more difficult.
Glaucoma (Blue Water)
Glaucoma causes damage to the optic nerve and is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. Lost vision cannot be restored, but medications, laser treatment, and surgery can help slow or stop the progression of the disease. Urgent surgical intervention may be required, especially if the condition does not respond to medications or laser therapy.
Can Cataracts Turn into Glaucoma?
Cataracts, commonly known as “white water in the eye,” develop due to the buildup of broken-down proteins in the natural lens, leading to clouding and reduced vision. Glaucoma, or “blue water,” on the other hand, is caused by increased fluid pressure inside the eye.
It is common for cataracts to develop after glaucoma surgery. For this reason, we usually recommend waiting at least one year after glaucoma treatment before undergoing cataract surgery.
In both conditions, early diagnosis and proper treatment generally lead to positive outcomes. However, cataracts do not usually require immediate intervention, while glaucoma is a serious condition that requires prompt medical consultation and treatment.
Types of Glaucoma
Glaucoma generally appears in two main forms:
Open-Angle Glaucoma (Most Common Type)
This is a chronic condition that progresses slowly over time, causing gradual loss of vision. It occurs when the aqueous fluid does not drain properly through the trabecular meshwork in the eye.
Angle-Closure Glaucoma (Less Common)
This is an acute condition that occurs in people who already have a narrow angle between the iris and cornea, where fluid normally drains. A sudden closure happens when the iris comes into contact with the cornea, blocking fluid flow.
It is characterized by sudden eye pain, a rapid increase in eye pressure, visual disturbances (such as seeing halos), and possible vision loss.
Important General Considerations
When planning glaucoma surgery, several important factors must be considered:
Patients are often older and may have multiple medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Children may also have congenital or genetic abnormalities.
Because these surgeries are relatively short, any existing medical conditions usually require only brief and careful management.
Glaucoma surgeries are extremely delicate, and increases in intraocular pressure (IOP) must be avoided. This includes avoiding certain medications, preventing coughing or straining, controlling nausea and vomiting, and avoiding Valsalva maneuvers. Otherwise, serious complications may occur, including expulsion of intraocular contents and potential blindness.
The patient’s glaucoma medications must be carefully reviewed due to possible interactions with anesthesia drugs.
Glaucoma – The Silent Thief of Sight
Glaucoma is known as the silent thief of vision because it often develops without noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages. Many patients do not realize they have the condition until significant vision loss has occurred. Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. It is a group of eye diseases in which increased eye pressure damages the optic nerve.
Currently, there is no cure for glaucoma. Therefore, treatment focuses on lowering eye pressure to slow the disease and prevent further vision loss. Early detection and proper management are essential to protect remaining vision.
So, what is the glaucoma treatment strategy at Batal Eye Specialty Center
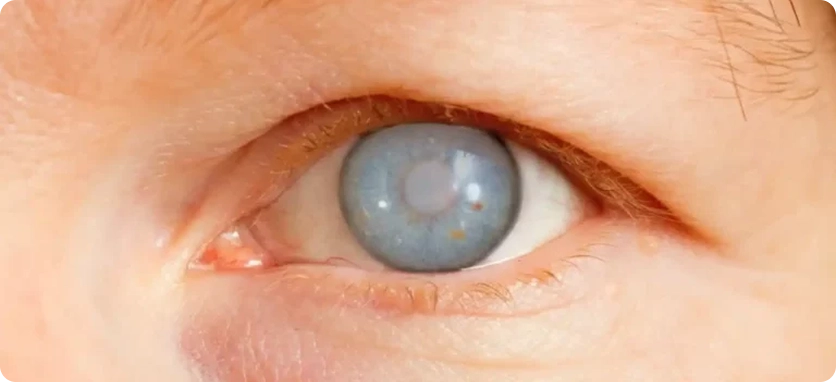
Symptoms of Glaucoma
Glaucoma may cause sudden and severe headache, nausea, blurred vision, and seeing halos around bright lights. Some patients may also experience a vague feeling of pressure or heaviness in the eye.
However, in many cases, glaucoma develops without noticeable symptoms, and patients may feel completely normal during early stages—even when visiting an eye doctor.
Can Cataracts Turn into Glaucoma?
Cataracts develop gradually with age and cause a progressive decline in vision. In the early stages, vision may become slightly blurred. Over time, it can feel as if there is a cloudy film over the eye, along with increased sensitivity to bright light and difficulty seeing at night. As the condition worsens, the pupil may change from its natural color to gray or white, and vision can become significantly impaired.
Cataracts form as proteins in the natural lens of the eye break down with age. Certain health conditions that are more common later in life—such as diabetes and high blood pressure—can accelerate this process, as well as the long-term use of certain medications.
Important note: Cataracts and glaucoma are two different conditions. Cataracts do not turn into glaucoma, but both can coexist and both require proper medical care to protect vision.
Glaucoma Treatment
Overview of Glaucoma Treatment
Glaucoma is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment once diagnosed. Early intervention is essential to reduce the risk of permanent vision loss. Most cases of glaucoma can be treated with eye drops, laser therapy, or microsurgery, depending on the severity and stage of the disease. The most effective treatment plan is determined after a thorough evaluation of each individual case.
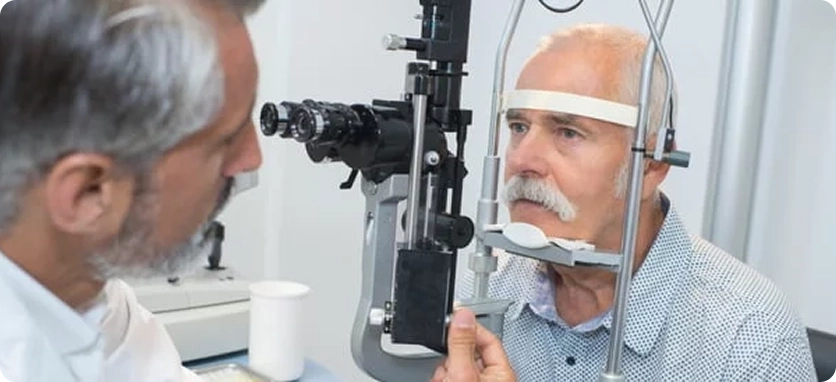
Glaucoma Treatment with Medication
Eye drops are commonly used to reduce fluid production in the eye or improve drainage of excess fluid that causes high eye pressure. However, they may sometimes lead to side effects such as eye redness, irritation, blurred vision, increased heart rate, dry mouth, and noticeable changes in eye color or the surrounding skin.
For this reason, patients should always inform their doctor if they have any allergies or sensitivities to medications to help minimize side effects. In some cases, the doctor may also prescribe additional medications in the form of tablets, syrup, or injections to better control eye pressure.
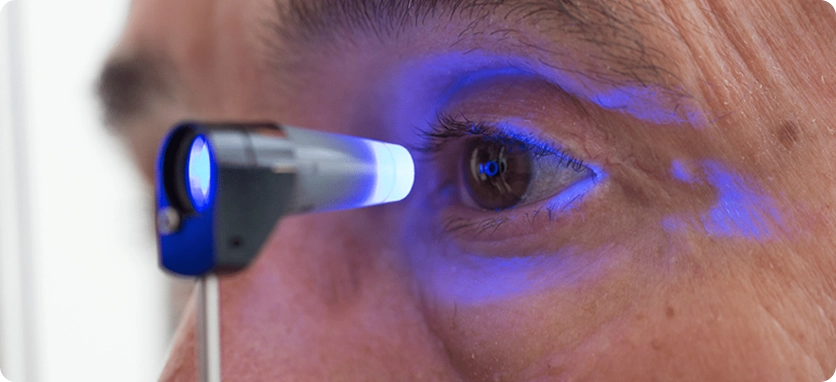
Laser Treatment for Glaucoma
At Batal Specialized Eye Center, we use laser therapy when eye drops are not effective in controlling glaucoma. By using low-energy laser beams, this procedure provides long-term results and offers a simple, minimally invasive solution to relieve glaucoma symptoms—without pain, scars, or significant side effects.
Laser treatment is an effective option for most patients and is especially suitable for those who find it difficult to use daily eye drops due to cost, discomfort, or side effects.
This procedure can help control glaucoma symptoms for several years without the need for additional medications and carries minimal risks or complications.
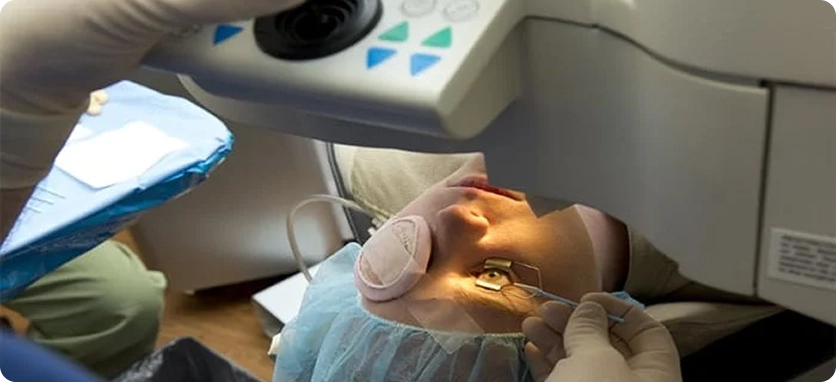
Microsurgery (Glaucoma Filtration Surgery)
Microsurgery is usually performed when medications and laser treatment fail to control glaucoma. The procedure helps drain the excess fluid inside the eye that builds up and puts pressure on the optic nerve, leading to glaucoma.
By reducing this pressure, microsurgery plays a critical role in protecting the optic nerve and preventing further vision loss.
Glaucoma Prevention
Although there is no guaranteed way to prevent glaucoma, regular eye examinations and early detection are the most effective ways to protect against vision damage caused by this condition. In addition, it is important to consider the following:
Excessive coffee intake (more than 2–3 cups per day) may increase eye pressure and is best avoided.
Patients with advanced glaucoma should avoid heavy weightlifting or strenuous exercises that increase pressure, such as certain yoga positions where the head is below the body.
Some people are at higher risk, including those over 60 years old, individuals with a family history of glaucoma, people with poor vision, and those with diabetes.
At Batal Specialized Medical Center, our specialists perform comprehensive eye evaluations, including measuring intraocular pressure, examining the optic nerve using OCT visual field testing, assessing corneal health, and performing detailed retinal examinations. In some cases, advanced imaging is used to obtain color images of the optic nerve to evaluate its size and condition. Based on your eye health, the doctor will recommend some or all of these tests.
Patients are advised to undergo a complete retinal examination at least once every two years, especially if they are at higher risk. With a specialized team in the treatment of both glaucoma and cataracts, supported by the latest diagnostic and treatment technologies, we are fully prepared to detect conditions early and provide comprehensive care and precise surgical treatment.
To learn more about cataract and glaucoma treatment and surgery, please contact us using the numbers provided.
What Tests Are Needed Before Surgery?
Since this procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, pre-operative testing is generally based on the patient’s medical history, physical condition, and current medications. In most cases, extensive routine testing is not required.
Studies have also shown that routine pre-surgical testing before glaucoma surgery does not significantly reduce the risk of complications or mortality compared to patients who do not undergo extensive testing.
Book an Appointment or Medical Consultation
Glaucoma Surgeries
Glaucoma surgeries include microsurgical trabeculectomy (with or without ExPRESS microshunt implantation), tube shunt implantation (a device used to drain excess eye fluid), and cyclophotocoagulation. There are also newer procedures known as MIGS – Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery. Each type of glaucoma surgery has its own specific indications, advantages, and limitations. When considering glaucoma surgery, it is essential to have a detailed discussion with your ophthalmic surgeon about the risks and benefits of the specific procedure recommended for your condition.
Types of Glaucoma Surgery
There are several types of glaucoma surgery, including:
Laser Treatment
Laser trabeculoplasty is one of the treatment options for patients with open-angle glaucoma. It is performed in the doctor’s clinic and uses a small laser beam to open blocked channels in the trabecular meshwork, helping fluid drain more effectively and lowering eye pressure.
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS)
Your doctor may recommend Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS) to help lower eye pressure. These procedures usually require less recovery time after surgery and carry fewer risks compared to traditional trabeculectomy or drainage implant surgery.
Filtering Surgery (Trabeculectomy)
In a procedure called trabeculectomy, the surgeon creates a small opening in the white part of the eye (sclera) and removes a portion of the trabecular meshwork. This allows excess fluid to drain out of the eye, helping to reduce eye pressure and protect the optic nerve.
Drainage Tubes (Tube Shunt Surgery)
In this procedure, the ophthalmic surgeon inserts a small tube shunt into the eye to help drain excess fluid and reduce intraocular pressure. This helps protect the optic nerve and prevent further vision loss.
Risk Factors for Glaucoma
The following factors increase the risk of developing glaucoma:
Family history of glaucoma
Age (60 years and older)
High intraocular pressure
Thin cornea
Severe nearsightedness (high myopia)
Previous eye surgery or eye injury
High blood pressure or cardiovascular disease
Diabetes
Use of corticosteroid medications
Glaucoma Diagnosis
Ophthalmologists check for glaucoma during a comprehensive eye examination. The Eye Center at Batal Specialized Medical Center in Saudi Arabia recommends having this exam every one to two years for people aged 65 and older.
Before the examination, the doctor may use eye drops to dilate or numb the pupils. Dilating the pupils allows more light to enter the eye and helps the ophthalmologist examine the eye more clearly.
The following tests may be part of a glaucoma evaluation:
Tonometry – uses a gentle air puff to measure eye pressure.
Pachymetry – measures the thickness of the cornea, the clear front part of the eye.
Visual Field Test – checks peripheral (side) vision.
Dilated Eye Exam – uses a light and magnifying lens to examine the optic nerve for damage.
Gonioscopy – uses a special mirrored lens to examine the angle between the cornea and the iris.

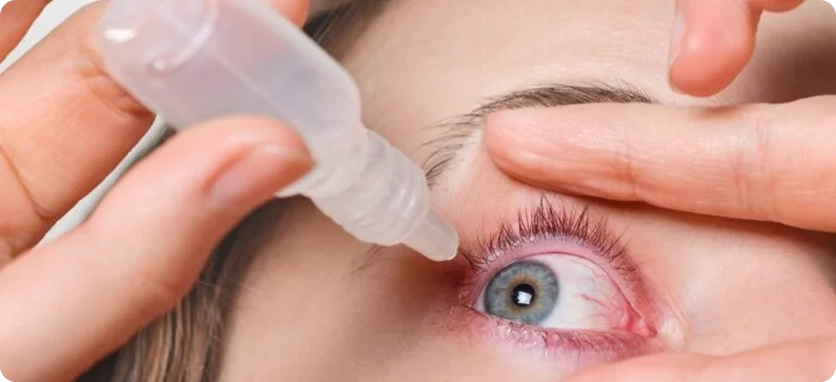
Glaucoma Treatment with Eye Drops
Eye drops are commonly used to lower intraocular pressure and help fluid drain more easily from the eye. These medications may include:
Prostaglandins
Rho kinase inhibitors
Nitric oxide donors
Miotic or cholinergic agents
Possible Side Effects
Some patients may experience side effects, including:
Burning or redness in the eyes
Dry mouth
Redness of the skin around the eyes
Blurred vision
Changes in energy levels, breathing, or heart rate
Best Glaucoma Surgeons at Batal Eye Specialty Center
Consultant in Glaucoma Surgery for Adults, Children, and Newborns | Cataract Surgery & Vision Correction
Specialty: Glaucoma Surgery & Cataract Surgery Academic Degree: Fellowship in Advanced Glaucoma Subspecialty from King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital – Riyadh
87 Reviews
Best Glaucoma Surgeons at Batal Eye Specialty Center
Batal Eye Specialty Center
Get Comprehensive Medical Care


Installments available up to 100% via Tamara & Tabby



